直線回歸 linear regression
2022-08-19
這部分只是範例後面才是正題(不知為何有時畫不出來,但分段執行plt.show()才能畫出來)
後來加工了30秒顯示
from sklearn import datasets
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import time
col_names = ['Sepal width', 'Sepal length', 'Petal with', 'Petal length']
df = pd.DataFrame(datasets.load_iris().data, columns=col_names)
sns.set(font_scale=1.5) # 字型大小
sns.pairplot(df) # 兩兩關系圖
plt.draw() #畫圖
plt.pause(10) #顯示30秒
plt.show(block=False)#顯示30秒關閉
plt.clf()#清除當前 figure 的所有axes,但是不關閉這個 window,所以能繼續復用於其他的 plot
sns.set(font_scale=1.5) #字型大小
print(df.corr())
sns.heatmap(df.corr(), annot = True, vmin=-1, vmax=1) # 熱圖
plt.draw() #畫圖
plt.pause(10) #顯示30秒
plt.show(block=False) #顯示30秒關閉
plt.clf()#清除當前 figure 的所有axes,但是不關閉這個 window,所以能繼續復用於其他的 plot
df_cols = df[['Sepal width', 'Sepal length']]
sns.set(font_scale=1.5)
sns.pairplot(df_cols,height=4) # 兩兩關系圖
plt.draw() #畫圖
plt.pause(10) #顯示30秒
plt.show(block=False) #顯示30秒關閉
直線回歸 用 DataFrame把圖畫出來
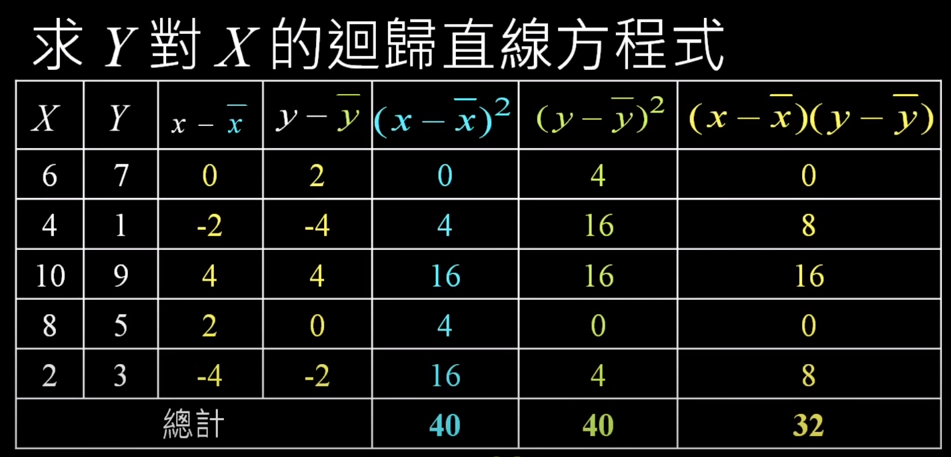
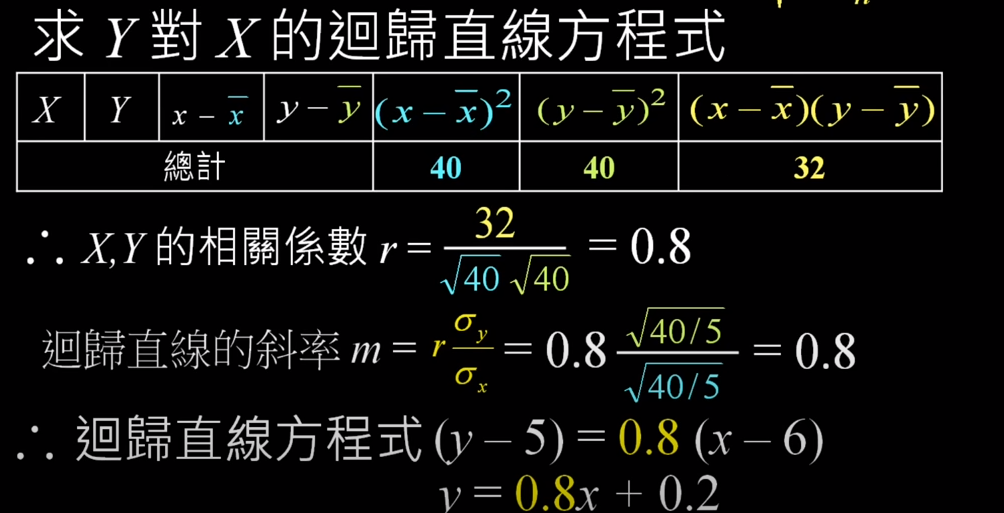
x = [6,5,10,8,2]
y = [7,1,9,5,3]
dat = {'X':x,'Y':y}
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(dat)
import seaborn as sb
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
sb.lmplot(x = "X", y = "Y", data = df)
plt.draw() #畫圖
plt.pause(10) #顯示30秒
plt.show(block=False) #顯示30秒關閉
計算式:
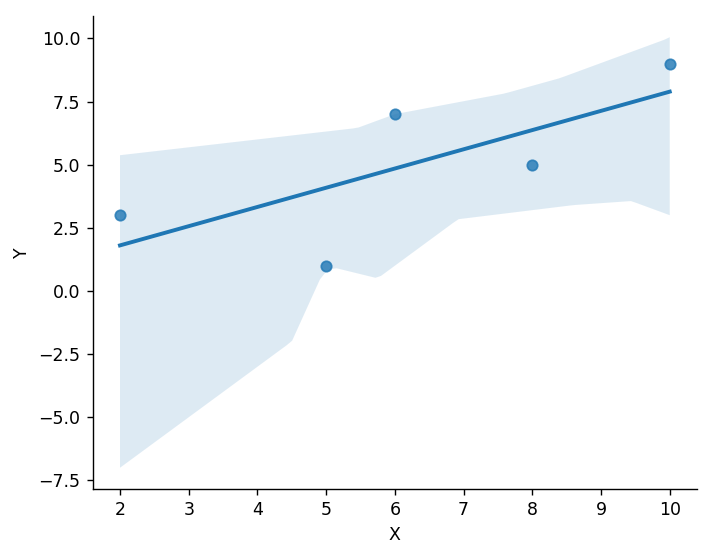

完全用 python 做 畫出來很棒
# correlation coefficient
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
length = np.array([4.7, 4.5, 4.9, 4., 4.6, 4.5, 4.7, 3.3, 4.6, 3.9, 3.5,
4.2, 4., 4.7, 3.6, 4.4, 4.5, 4.1, 4.5, 3.9, 4.8, 4.,
4.9, 4.7, 4.3, 4.4, 4.8, 5., 4.5, 3.5, 3.8, 3.7, 3.9,
5.1, 4.5, 4.5, 4.7, 4.4, 4.1, 4., 4.4, 4.6, 4., 3.3,
4.2, 4.2, 4.2, 4.3, 3., 4.1])
width = np.array([1.4, 1.5, 1.5, 1.3, 1.5, 1.3, 1.6, 1., 1.3, 1.4, 1.,
1.5, 1., 1.4, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1., 1.5, 1.1, 1.8, 1.3,
1.5, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.4, 1.7, 1.5, 1., 1.1, 1., 1.2,
1.6, 1.5, 1.6, 1.5, 1.3, 1.3, 1.3, 1.2, 1.4, 1.2, 1.,
1.3, 1.2, 1.3, 1.3, 1.1, 1.3])
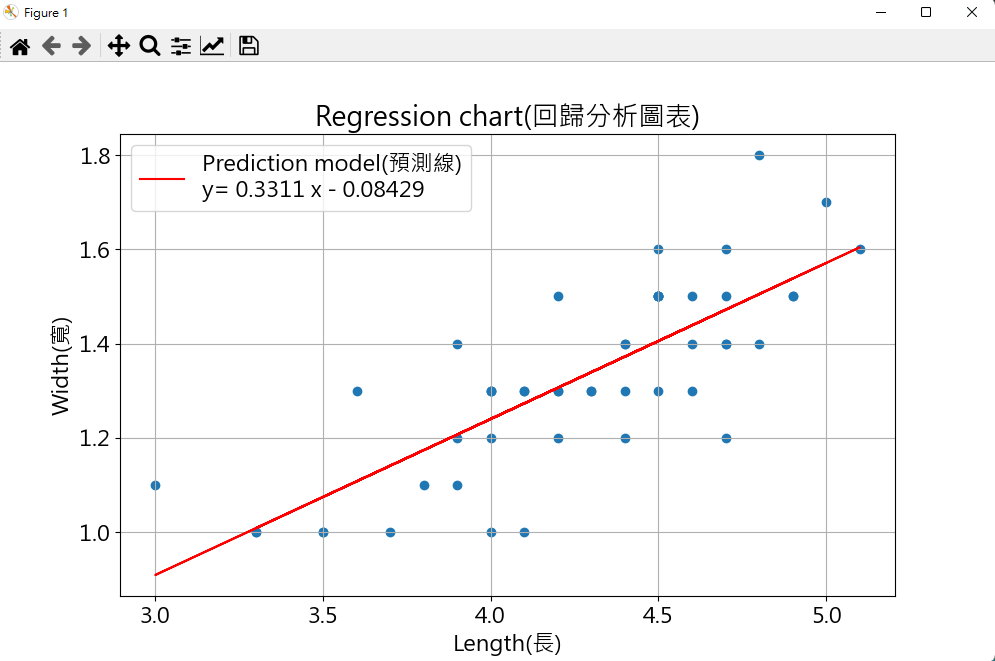
print(np.corrcoef(length,width).round(4)) #相關矩陣(Correlation Matrix) round是四捨五入
print(np.polyfit(length,width,1).round(4)) #回歸係數矩陣(round是四捨五入) Y = AX + B
coef = np.polyfit(length,width,1) #回歸係數矩陣
reg_model = np.poly1d(coef) #回歸模型
print (reg_model) # 印出回歸模型
print (reg_model(6).round(1)) # 輸入 length 預測出 width
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6)) # 設定圖大小(吋)
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'Microsoft JhengHei' # 字形微軟正黑體
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 16 #字形大小
plt.scatter(length,width) #分散點圖
plt.plot(length, reg_model(length), color='red', label='Prediction model(預測線)\n'+'y='+str(reg_model).replace('\n','')) # 回歸模型的線
plt.title('Regression chart(回歸分析圖表)') # 設定標頭
plt.xlabel('Length(長)') # 設定X軸文字
plt.ylabel('Width(寬)') # 設定y軸文字
plt.legend() #顯示圖例
plt.grid(True) #顯示格線
plt.show() # show plt 圖
plt.bar(length,width) #長條圖
plt.show() # show plt 圖
plt.pie(length,labels=width, autopct='%1.1f%%') #圓餅圖(資料, 標籤, 百分比標示)
plt.show() # show plt 圖
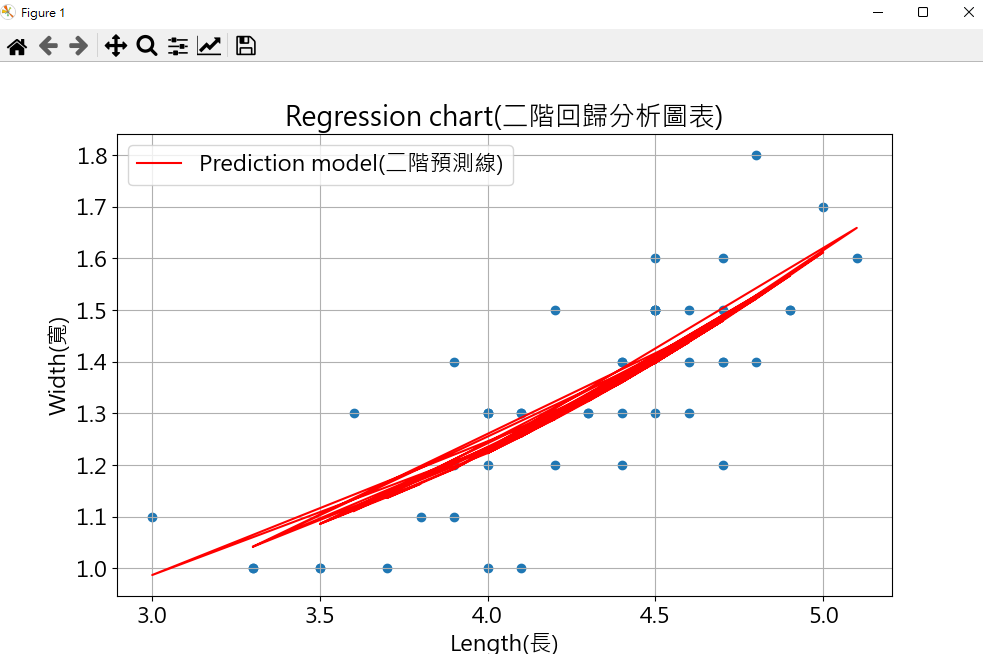
print(np.corrcoef(length,width).round(4)) #相關矩陣(Correlation Matrix) round是四捨五入
print(np.polyfit(length,width,2).round(4)) #回歸係數矩陣(round是四捨五入) Y = AX + B
coef = np.polyfit(length,width,2) #回歸係數矩陣
reg2_model = np.poly1d(coef) #回歸模型
print (reg2_model) # 印出回歸模型
print (reg2_model(6).round(1)) # 輸入 length 預測出 width
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6)) # 設定圖大小(吋)
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'Microsoft JhengHei' # 字形微軟正黑體
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 16 #字形大小
plt.scatter(length,width) #分散點圖
plt.plot(length, reg2_model(length), color='red', label='Prediction model(二階預測線)') # 回歸模型的線
plt.title('Regression chart(二階回歸分析圖表)') # 設定標頭
plt.xlabel('Length(長)') # 設定X軸文字
plt.ylabel('Width(寬)') # 設定y軸文字
plt.legend() #顯示圖例
plt.grid(True) #顯示格線
plt.show() # show plt 圖
plt.bar(length,width) #長條圖
plt.show() # show plt 圖
plt.pie(length,labels=width, autopct='%1.1f%%') #圓餅圖(資料, 標籤, 百分比標示)
plt.show() # show plt 圖